Toshiba recently introduced an analog output IC optocoupler, the TLX9309, which is AEC-Q101 compliant and suitable for automotive applications, providing high-speed communications for automotive applications, particularly electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles.
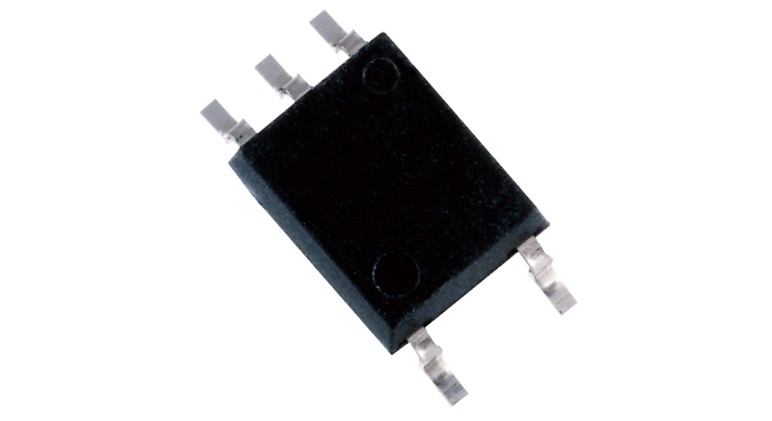
The TLX9309 consists of a high output GaAlAs light emitting diode (LED) that is optically coupled to a high-speed detector. The detector consists of a photodiode and a transistor integrated on a single chip. Faraday shields have been integrated into photodetector chips to provide a higher level of common mode transient immunity - typically up to 15kV /μs, which is an important parameter in an automotive noise automotive environment.
By separating the photodiode and the amplifying transistor, the collector capacitance is reduced, reducing the propagation delay, making the open collector TLX9309 faster than the transistor output device. In fact, the propagation delay time is guaranteed to be between 0.1μs and 1.0μs, and the difference between high and low variations and low-to-high transitions (|tpLH-tpHL |) does not exceed 0.7μs, making the device suitable for high-speed communication, such as Inverter control or as an interface to an intelligent power module (IPM).
Electrically, the device provides 3750Vrms isolation, 5.0mm creepage distance and clearance for safe isolation. It operates from a supply range of -0.5 to 30V DC and can drive up to 25mA at output voltages up to 20V. The current transfer rate is in the range of 15-300%.
The TLX9309 is available in a 3.7mm x 7.0mm x 2.2mm RoHS-compliant, 5-lead SO6 package and operates over the -40°C to +125°C temperature range.










All Comments (0)