Application drives the price increase of passive electronic components
In the past two years, when Japanese and Korean manufacturers adjusted their product mix, the market demand for passive components gradually increased, leading to shortages and price increases for passive components. The products mainly involved MLCC (multilayer ceramic capacitors) and R-Chip (chip resistors). The biggest price increase is the high-end MLCC products with small size and large capacity. Some of the models have increased by dozens of times in the spot market, followed by conventional consumer electronics MLCCs and R-chips.
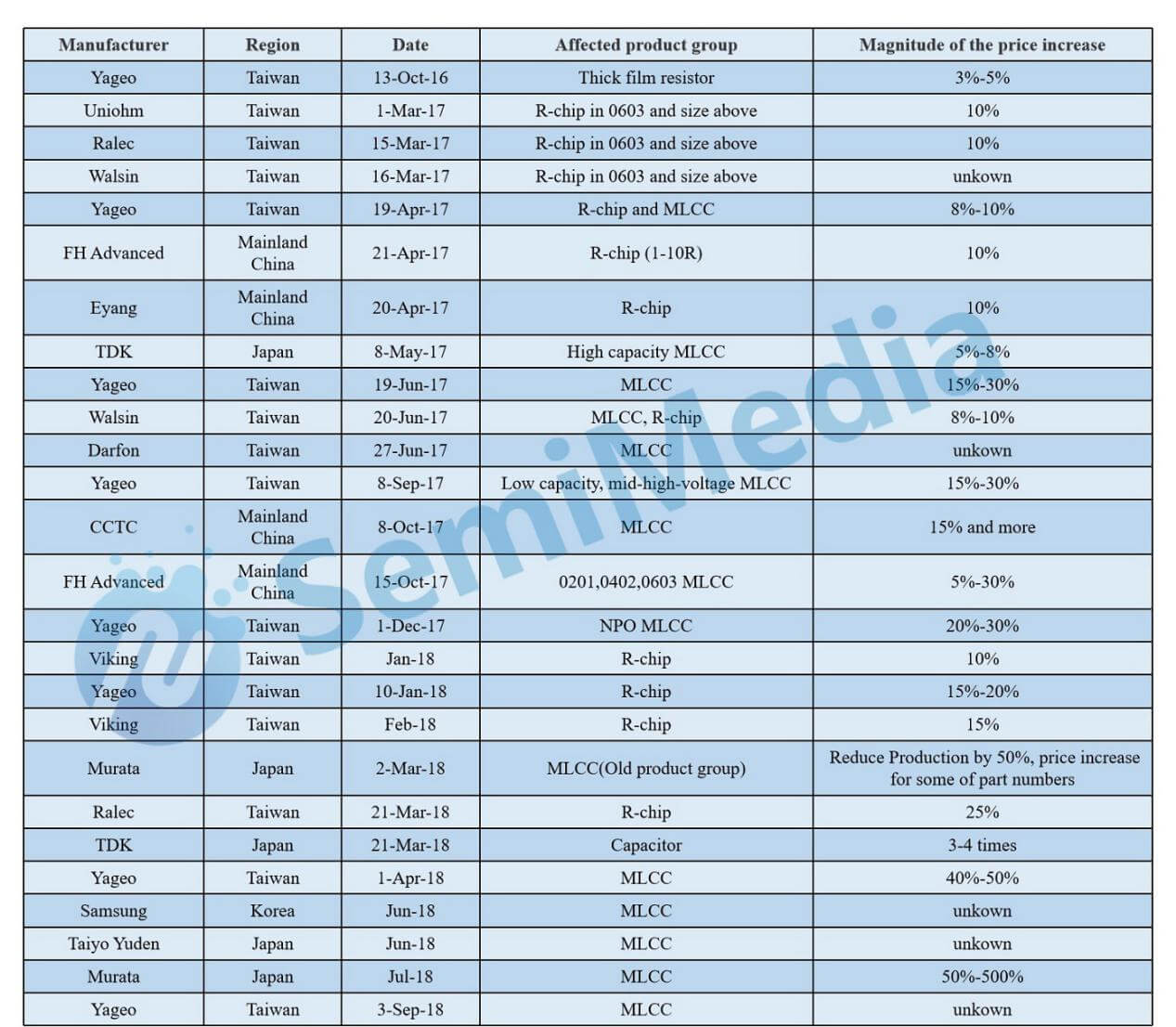
Price increases information of various manufacturers since 2016
From the development history of passive components, the changes and development of the downstream application market dominate the development of the passive component market. In addition, capital expenditure and technology upgrade are also important driving forces for the development of passive components. Passive components are the cornerstone of the development of the electronics industry. In terms of market size, the passive component market reached US$25 billion in 2017 and is expected to reach US$32.89 billion in 2021. The main application fields of passive components are consumer electronics, automotive electronics, home appliances, etc., of which consumer electronics account for more than 70%.
From the application side, the consumer electronics upgrades, new technologies and 5G applications have combined to drive the demand for passive components to increase further. In the past few years, the global smartphone market has expanded rapidly. Although the current growth rate has slowed down, it is expected that there will be some increase in the future. The increase in shipments of terminal electronic products represented by mobile phones has a positive effect on the sales of passive components.
The upgrade of smartphone functions has promoted the integration of chips and promoted the development of miniaturization of passive components. At the same time, the use of MLCCs for single handsets has rapidly increased. Take iphone as an example, in early 2007, the iphone single-machine MLCC usage was only 177 pieces, in 2016, the phone 7 had reached 890 pieces, and the iphone X was as high as 1,100 pieces.
Different from the consumer electronics, automotive electronics have higher security requirements and more market segments. Advances in automotive electronics have driven the development of passive components to high-end and refined. The high-performance passive components of automotive electronics have achieved rapid development and are gradually replacing low-end passive components. Passive components for vehicles must be able to withstand harsh environments such as high temperatures, strong vibrations, and shocks.
Automotive electronics are mainly used in power control systems, in-vehicle infotainment systems, car safety control systems and body electronics systems. In order to improve the driving experience, the electronic rate of automobiles is constantly increasing. According to the research and testing center, the average amount of passive components of automobiles will exceed 5,000 pieces.
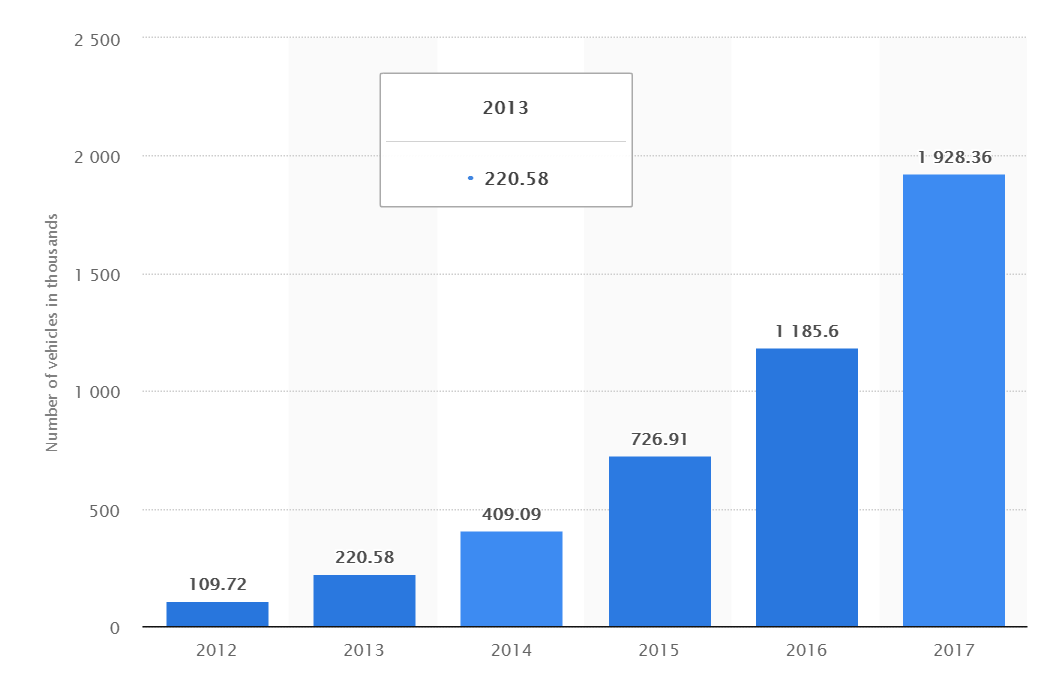
Worldwide number of battery electric vehicles in use from 2012 to 2017
Source: Statista
In addition, new energy vehicles (electric vehicles) will further increase the electronic rate of automobiles and drive the expansion of the market for passive components for vehicles. In recent years, driven by Tesla, the global new energy vehicle market has developed rapidly, and the annual output of electric vehicles is rising. With the policy of supporting new energy vehicles in various countries, the output of new energy vehicles will further increase. The cost of electronic components of new energy vehicles is much higher than that of traditional vehicles. The increase in production of new energy vehicles will effectively drive the market size of passive components for automotive applications.
Based on this background, Japanese passive component manufacturers in the high-end market have taken the lead in adjusting production capacity and deploying more capacity in automotive electronics, industrial miniaturization, high-profile products and RF components. Upgrade the product structure and gradually reduce or cancel the production of low-end products. As Japanese manufacturers have the largest market share in the global market, each strategic adjustment will affect global market trends. So, how does the passive electronic components industry in Japan develop step by step into today's market position?
The rise of Japan's passive component industry
The Japanese electronics industry rose rapidly after World War II, in addition to favorable factors and strategies such as increased demand for electronic products in Japan after the war, strong Japanese manufacturers' innovation and technological strength, and active expansion of overseas territory. There is also a deeper development logic behind it: the Japanese government's active economic policy and strategic trade incentives, and the international electronics industry environment is also extremely beneficial to Japan.
The Japanese government reforms the import tariff structure according to different stages of development and the international environment in the country, adopts a lower tariff level for raw materials, and adopts high tariffs on imported electronic products, opening up sufficient room for growth for local enterprises, promoted the development of the local passive component manufacturers. On the other hand, the government's support for the domestic oligarchs is also a very important factor, turning a blind eye to the joint monopoly between enterprises, and even allowing the Sogo shosha (general trading companies) to be free from the monopoly law in the form of law. It has promoted the rapid development of the entire electronics industry chain including passive components manufacturers such as TDK and Murata, and improved their respective international competitiveness.
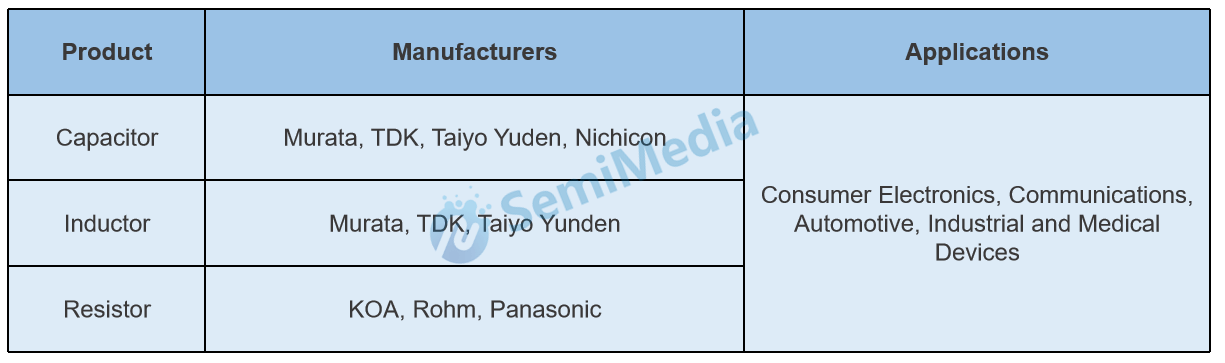
Japanese passive component industry chain
After the heyday of the 1990s, the Japanese electronics industry was gradually replaced by countries such as South Korea, and traditional strong industries such as consumer electronics, semiconductors, and home appliances were greatly affected. The acquisition of Toshiba's flash memory business marks the end of an era, but Japanese electronic component manufacturers have grown rapidly in the era of smart phones with their deep technical barriers, forming seven major industry giants: Kyocera, TDK, Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd., NIDEC CORPORATION, Nitto Denko, Alps Electric, Rohm.
The reason why Japanese manufacturers succeeded was that electronic components were different from other industries such as consumer electronics. The production of electronic components required extremely high material quality, and only good materials could make good components. Japan leads a lot in materials technology, so it is difficult for manufacturers in other regions to surpass Japanese manufacturers. Secondly, the production process of electronic components requires a long time to explore and accumulate Know-How, which is highly consistent with the Japanese craftsman spirit and corporate culture. Thirdly, a highly sophisticated downstream support. Japan adopts a directional and concentrated strategy to actively deploy high-end automotive electronics, robotics and high-end manufacturing, industrial control, aerospace and other high-end industries, these strong industrial demands have made the manufacturing process more advanced and refined.

The seven giants of Japan's passive component industry
Capacitor market competition pattern and Japanese manufacturers
The main functions of capacitors are charge storage, AC filtering, cutting off or blocking DC voltage, providing tuning and oscillation, etc., which are widely used in the circuit of DC-blocking, coupling, filtering, tuning loop, energy conversion, control and so on.
At present, in the passive component market, Japan is the region with the highest proportion and quality. The industry leaders Murata and TDK last year earned more than $10 billion in passive components, accounting for almost half of the market. American manufacturers also actively developed passive components after World War II. The two passive component giants, Vishay and Kemei, occupied a place in the field of passive components through multiple mergers and acquisitions. South Korea's Samsung developed the ultra-small MLCC in 1988, and it did not start to expand significantly for MLCC until 2007. Passive component manufacturers in Taiwan are balanced. Passive components in mainland China are mainly dominated by medium and low-end products, but a number of high-quality manufacturers have emerged.
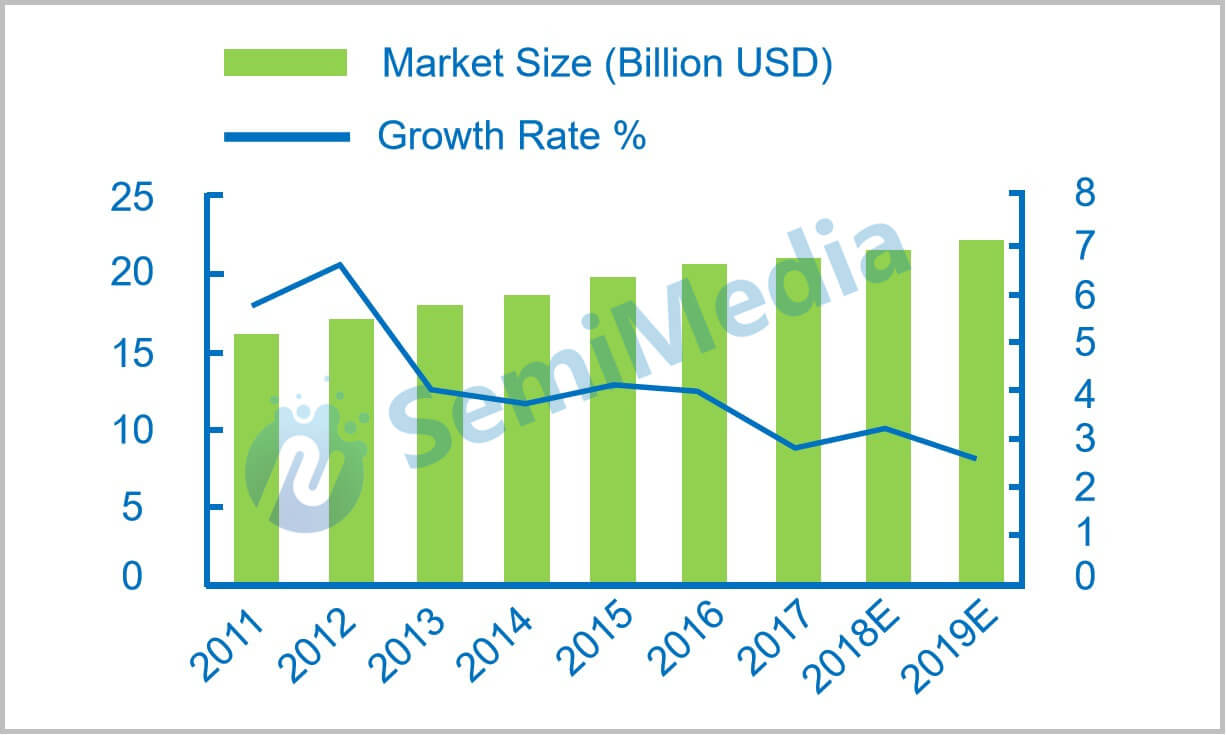
Global market size of capacitors
In 2017, the global capacitor market was 20.9 billion US dollars. At present, the global capacitor industry is dominated by Japan, the United States, and China. Among them, Japan is in a leading position, monopolizing high-end components, and has the strongest strength in electrolytic capacitors, ceramic capacitors, and film capacitors.
Capacitors can be divided into dielectric capacitors, film capacitors, aluminum electrolytic capacitors, tantalum electrolytic capacitors, and super capacitors. From the global market share in 2015, the output value of ceramic capacitors and aluminum electrolytic capacitors is relatively high, with ceramic capacitors accounting for 54%, aluminum electrolytic capacitors for 23%, and film capacitors and tantalum capacitors accounting for 11% and 12%, respectively.
Ceramic capacitors are superior to traditional aluminum electrolytic capacitors in terms of lifetime, volume, ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance), and voltage range. With the advent of large-capacity ceramic capacitors, aluminum electrolytic capacitors with capacities below 100uF have been gradually replaced, and large-capacity ceramic capacitors of more than 300uF have been gradually developed.
Ceramic capacitors can be classified into single-layer ceramic capacitors, MLCC, and leaded multilayer ceramic capacitors. In addition to the capacitive characteristics of "straight through", MLCC has other features such as large capacity, long life, high reliability, low ESR, high temperature and high pressure resistance, small size, wide capacitance range, suitable for surface mounting. Both cost and performance have a considerable advantage.
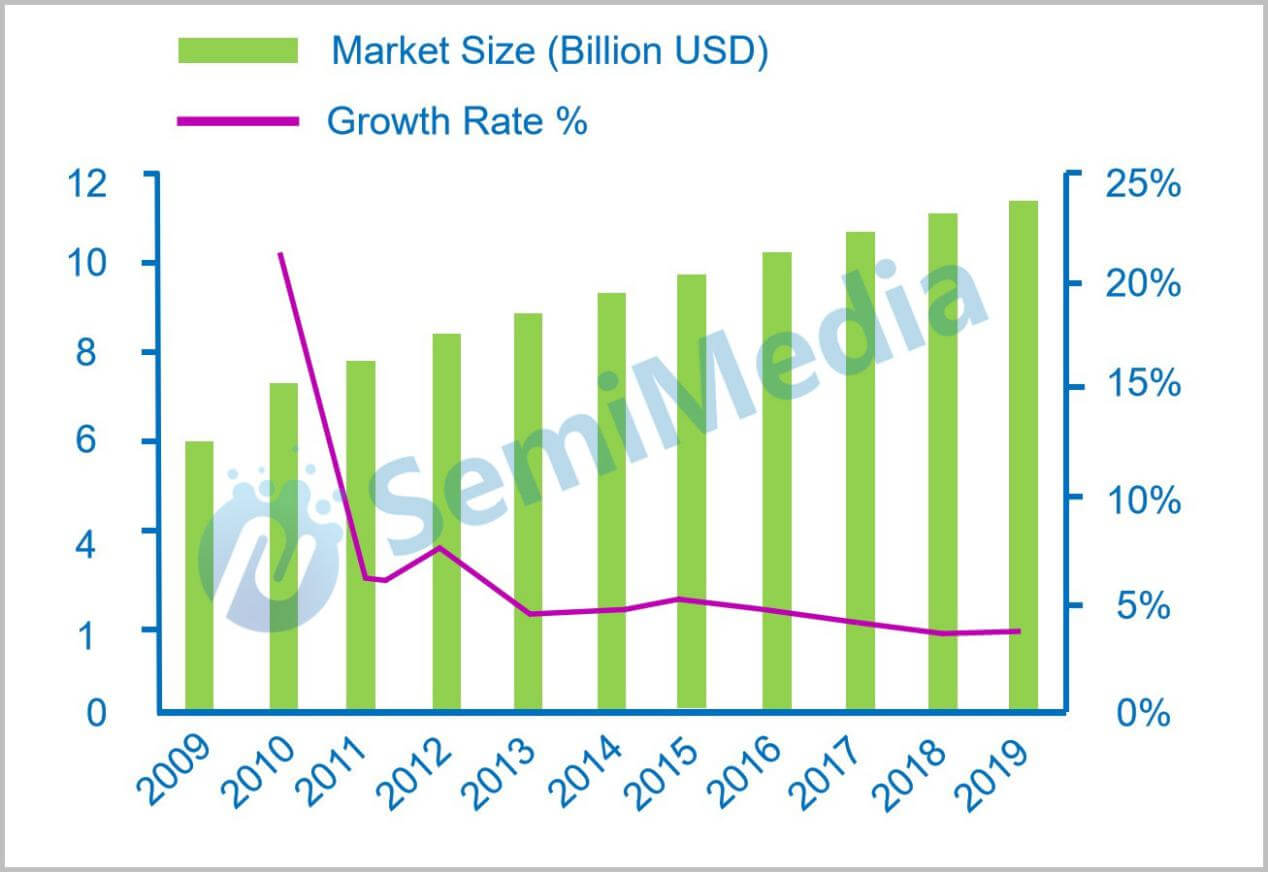
Global market size of MLCC
The world's major MLCC manufacturers include Murata, Taiyo Yuden, Kyocera and TDK from Japan; Kemet from the United States; Samsung in South Korea; Yageo, Walsin and HolyStone in Taiwan; Eyang, CCTC and Fenghua Advanced in mainland China. Among them, the top five manufacturers are Murata, Samsung, Yageo, Taiyo Yuden and TDK, which together account for 85% of the total market share. The MLCC products in mainland China are still in their infancy and have growth potential.
There is no doubt that Japan's passive component industry chain cannot be replaced, so when its market strategy is adjusted, it indirectly creates a supply gap for low-end passive components. The industry generally believes that this is the fuse of MLCC and R-chip shortages and price increases in the past two years. (to be continued)
Please stay tuned for the next article in the "Japan's dominant position in the passive electronics component market" series: Footprints of Murata.










All Comments (0)